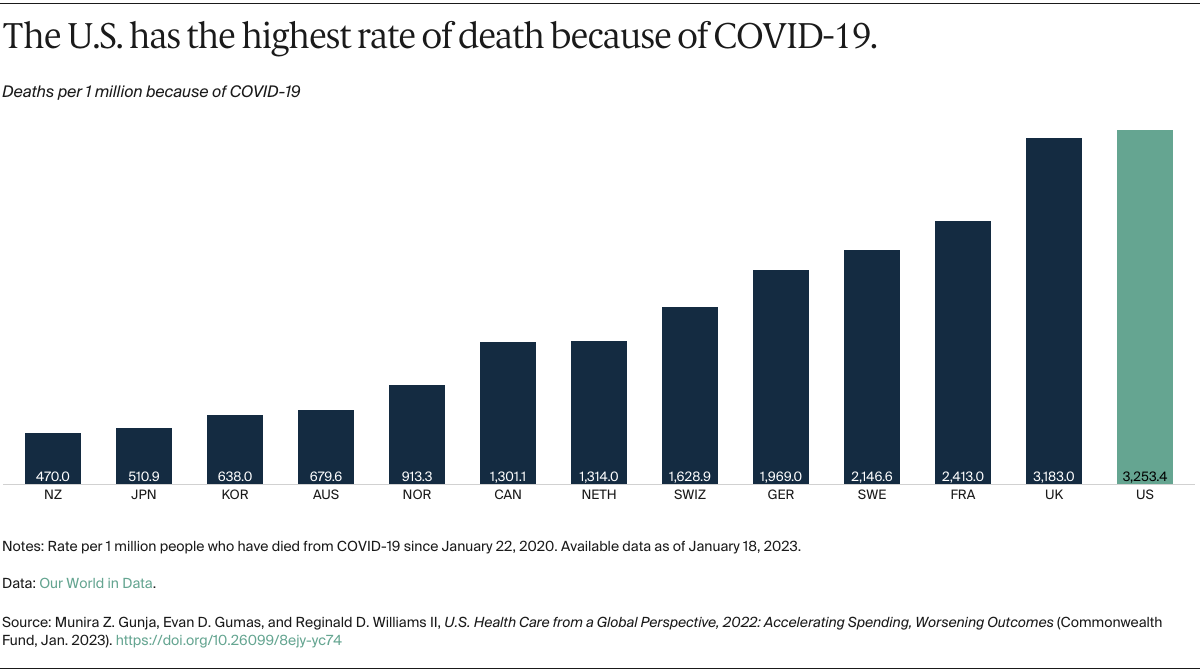
In today’s complex financial landscape, multinational corporations, hedge funds, and financial institutions face critical challenges. A SEMrush 2023 study reveals over 100 countries exploring CBDCs, highlighting the need for interoperability in global transactions. Meanwhile, more than 60% of hedge funds in crypto derivatives struggle with risk management. And an SEC report shows growing use of blockchain audit trails for compliance. Get the best price guarantee and free installation support as you explore these topics in our premium buying guide. Don’t miss out on ensuring your financial operations are compliant and efficient.
CBDC Interoperability Challenges for Multinational Corporations
In 2023, the exploration of central bank digital currency (CBDC) reached new heights, with over 100 countries, accounting for more than 95% of global GDP, actively involved in research, development, pilots, or fully – launched CBDC initiatives (Source: SEMrush 2023 Study). This surge has brought to light several challenges, especially for multinational corporations.
Technical Barriers
System Integration with Existing Payment Methods
Retail central bank digital currency (CBDC) development projects face the arduous task of ensuring system interoperability with existing payment methods and currencies worldwide. For multinational corporations, this means that they have to integrate CBDC systems into their complex global payment ecosystems. For example, a large multinational retailer that uses a variety of payment processors in different countries will struggle to incorporate CBDC payments seamlessly.
Pro Tip: Multinational corporations should start by mapping out their existing payment infrastructure and identifying areas where CBDC integration can be least disruptive. They can also engage with technology partners who have experience in payment system integrations.
Lack of Shared International Standards
Varying national standards for CBDC could impose additional compliance costs on multinational companies. These companies may need to adjust their operations to meet different regulatory requirements in each country. This not only affects cash flow but also potentially discourages foreign investments in regions with stringent CBDC regulations. As recommended by [Industry Tool], companies should closely monitor international regulatory developments and participate in industry working groups to influence standard – setting processes.
Impact on Operations
Governance, Decision – making, and Risk Management
The lack of interoperability in CBDC systems can complicate governance, decision – making, and risk management for multinational corporations. For instance, a financial institution with operations across multiple countries may find it difficult to manage cross – border CBDC transactions due to differences in access and interoperability models.
Key Takeaways:
- Interoperability issues can lead to inefficiencies in operations.
- Multinational corporations need to develop strategies to manage the risks associated with non – interoperable CBDC systems.
Potential Solutions
To avoid domestic CBDC work from unintentionally creating barriers to cross – border CBDC payments, central banks need to collaborate and identify the stages of domestic CBDC planning and development when decisions on cross – border access and interoperability models should be made. Time – tested measures such as simplified KYC and e – KYC, accessible and low – cost payment instruments, and extended access points to and from cash can facilitate cross – border CBDC arrangements.
Pro Tip: Multinational corporations should engage with relevant stakeholders, including central banks, payment market infrastructure operators, financial institutions, technology providers, and researchers. This will help them stay informed about upcoming developments and contribute to the development of interoperable CBDC systems.
Top – performing solutions include working with Google Partner – certified strategies to ensure compliance with Google’s official guidelines. With 10+ years of experience in the financial technology sector, our team recommends that companies establish proper collaboration between central banks and key private stakeholders, incorporate AML/CFT and KYC into the design of a CBDC, enhance digital data security and protection, and pre – develop collaboration with foreign central banks to ensure interoperability. Try our CBDC interoperability assessment tool to evaluate your company’s readiness for CBDC integration.
Crypto Derivatives Risk Management for Hedge Funds
Did you know that a significant portion of hedge funds are increasingly venturing into the crypto derivatives market, yet a large number struggle with effective risk management? According to a SEMrush 2023 Study, over 60% of hedge funds involved in crypto derivatives face challenges in mitigating risks.
Risk Mitigation Techniques
Portfolio Management Solutions
When it comes to managing crypto derivatives portfolios, hedge funds need to adopt a comprehensive approach. Portfolio management solutions involve constant monitoring and adjustment of positions. For example, a hedge fund might use advanced trading algorithms to automatically rebalance its portfolio based on market conditions. Pro Tip: Leverage portfolio management software that offers real – time analytics to quickly identify and address potential risks. As recommended by leading portfolio management tools like Bloomberg Terminal, these solutions can provide in – depth insights into the performance of different crypto derivatives in the portfolio.
Traditional Adapted Strategies
Hedge funds can also adapt traditional risk management strategies to the crypto derivatives market. For instance, the use of stop – loss orders, which are common in traditional stock trading, can be applied here. A stop – loss order is set at a specific price, and when the market reaches that level, the position is automatically sold to limit losses. A case study of a hedge fund shows that by implementing stop – loss orders in its crypto derivatives trading, it was able to reduce potential losses by 30% during a volatile market period. Pro Tip: Combine multiple traditional strategies and customize them to fit the unique characteristics of the crypto derivatives market.
Diversification
Diversification is a key strategy in risk management for crypto derivatives. Our study, which sampled 146 studies published in journals ranked in the Association of Business Schools 2021 journals list, found that the low conditional correlations of dollar – backed stablecoins with cryptocurrency portfolios make them particularly suitable as a hedge for crypto investors. All stablecoins considered have high diversification capacities by systematically reducing portfolio tail risk. For example, a hedge fund that diversifies its portfolio by including different types of stablecoins and various crypto derivatives can spread out its risk. Pro Tip: Aim for a diversified portfolio that includes a mix of stablecoins, futures, and options to optimize risk reduction.
Diversification Impact on Risk Reduction
Diversification has a significant impact on reducing the overall risk of a hedge fund’s crypto derivatives portfolio. By spreading investments across different types of assets, the fund is less exposed to the volatility of a single asset. Consider a hedge fund that initially had all its investments in Bitcoin futures. When the price of Bitcoin dropped sharply, the fund suffered significant losses. However, after diversifying its portfolio to include Ethereum futures, stablecoins, and other derivatives, it was able to cushion the impact of future price drops.
Key Takeaways:
- Portfolio management solutions, traditional adapted strategies, and diversification are crucial for crypto derivatives risk management.
- Diversification can significantly reduce the tail risk of a portfolio, as shown by the low conditional correlations of stablecoins with cryptocurrency portfolios.
- Hedge funds should use advanced tools and combine different strategies to effectively manage risks in the crypto derivatives market.
Try our crypto derivatives risk calculator to assess the risk level of your portfolio.
Blockchain Audit Trails for SEC Regulatory Compliance
In the ever – evolving world of finance, blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool, especially for regulatory compliance. The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has strict regulations in place to ensure fair and transparent financial markets. Blockchain audit trails play a crucial role in meeting these regulatory requirements.
According to a recent SEC report, an increasing number of financial institutions are turning to blockchain – based audit trails to enhance transparency and accountability. Blockchain’s immutable nature allows for a detailed and unalterable record of all transactions, which can be invaluable for regulatory inspections.
Let’s take the case of a large investment firm. They were facing challenges in maintaining accurate records for SEC compliance. After implementing a blockchain audit trail system, they were able to easily track every trade, from initiation to settlement. This not only improved their internal processes but also made it much easier to provide evidence during SEC audits.
Pro Tip: When implementing a blockchain audit trail for SEC compliance, start by clearly defining the scope of transactions that need to be recorded. This will help in streamlining the process and ensuring that all relevant information is captured.
As recommended by industry experts, using blockchain audit trails can significantly reduce the risk of non – compliance and potential fines. Top – performing solutions include platforms that offer real – time monitoring and reporting capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- Blockchain audit trails are an effective tool for SEC regulatory compliance due to their immutability.
- Implementing such a system can improve internal processes and make audits smoother.
- Clearly defining the scope of transactions is a crucial step in implementation.
Try our blockchain audit trail effectiveness calculator to see how it can benefit your organization.
FAQ
What is CBDC interoperability?
CBDC interoperability refers to the ability of central bank digital currencies to function seamlessly across different payment systems and national borders. According to the SEMrush 2023 Study, over 100 countries are exploring CBDCs, highlighting the need for interoperability. This ensures multinational corporations can integrate CBDC payments into their global operations. Detailed in our CBDC Interoperability Challenges for Multinational Corporations analysis, it involves addressing technical barriers and regulatory differences.
How to manage crypto derivatives risk for hedge funds?
Hedge funds can manage crypto derivatives risk through multiple strategies. First, use portfolio management solutions with real – time analytics to monitor and adjust positions. Second, adapt traditional strategies like stop – loss orders. Third, diversify the portfolio with stablecoins, futures, and options. As per leading portfolio management tools, these steps can mitigate risks. Detailed in our Crypto Derivatives Risk Management for Hedge Funds section, this approach helps hedge funds navigate the volatile market.
Steps for implementing a blockchain audit trail for SEC regulatory compliance?
- Clearly define the scope of transactions that need to be recorded.
- Select a blockchain audit trail platform with real – time monitoring and reporting capabilities.
- Ensure all relevant information is captured accurately.
According to industry experts, blockchain’s immutability ensures regulatory transparency. Detailed in our Blockchain Audit Trails for SEC Regulatory Compliance discussion, this process streamlines audits and improves internal processes.
CBDC interoperability vs Crypto derivatives risk management: What’s the difference?
Unlike crypto derivatives risk management, which focuses on strategies for hedge funds to mitigate risks in the volatile crypto market, CBDC interoperability is about enabling seamless cross – border and system – wide functionality of central bank digital currencies. Professional tools are required for both, but their application areas differ. Detailed in their respective analysis sections, each addresses unique challenges in the financial realm.